
State of the Art Technology Center

We think along with you about your process, define each others issues and optimize the process from there out. In this way the process will be better, more smart and efficient, resulting in a much higher and more consistent quality.
Jongia’s (inhouse) Technology Center enables us to finetune your process to guarantee the best possible results. In close collaboration with our R&D team, our customers have been able to achieve considerable process improvements.
Process Technology
Single phase liquid blending/mixing (L-L)
In single phase liquid blending, two miscible liquids are blended together to form a single liquid mixture. The intensity of mixing two liquids depends on the liquid volume fractions in the final product, the densities and viscosities of the liquids. The molecules of the two liquids dissolve in each other, which creates a single homogeneous phase. Depending on the degree of mixing, several degrees of blending between two liquids can be achieved. A typical application of this type of system is the blending of different gasoline feedstocks to obtain the right reaction mixture.
Multiphase liquid blending/emulsification (L – L)
Emulsification is the process of mixing two immiscible liquids into each other. Liquids are often immiscible due to the polarity of the involved molecules. For example, water is a very polar liquid while hexane is very apolar due to the carbon chain. The molecules of the different liquids tend to stay together instead of form one mixture. Two immiscible liquids can be mixed by changing one of the liquids into a phase of extremely small particles. These particles are dispersed over the other continuous liquid phase to produce a homogeneous multiphase flow. These multiphase flows require continuous mixing as the particles tend to agglomerate and separate from the continuous liquid phase. Examples of emulsification processes are the production of mayonnaise and milk.
Solvation of solids (S – L)
In this process, solids are dissolved in a fluid to create a new solution of solvent and dissolved molecules. Often in these processes, a molecule is dissociated into its corresponding ions. The ions are stabilized by the solvent to form a solution. Mixers serve a dual function in these types of systems. Mixers can cleave crystals/powders, increasing the contact area between solvent and solid. In addition, the mixer can distribute the solid and dissolved molecules over de solvent phase to obtain a uniform concentration. Examples of applications are the solvation of glucose crystals and the dissolving of salts.
Gas dispersion (G – L)
A dispersion can also consist of a gas phase suspended in a liquid continuous phase. The gas is bubbled into the liquid phase at the bottom of the tank. Gas dispersion can increase the contact area between gas and liquid by breaking apart gas bubbles into multiple smaller bubbles. The mixer also works to distribute the gas evenly over the liquid phase. Additionally, the mixer provides a uniform distribution over the liquid phase and can increase contact time due to the induced flow profiles. These systems are often applied in multiphase reactions of gasses and liquids. Typically, the gas dissolves in the liquid so it can react with the reactant in the liquid. Contact area and time are important as the mass transfer limitation is often in the transfer from gas to liquid.
Heat- and energy transfer
All the other described processes are examples of mixers providing solutions to mass transfer problems. However, mixers can also assist in the transfer of energy (heat). This is especially the case in liquid phases, where heat transfer can be significantly improved by agitation. In a stagnant liquid, energy transfer occurs due to diffusion and free convection in the phase. Agitation of the liquid phase induces flow profiles, which stimulates the transfer of energy due to the addition of forced convection phenomena to the system. Additionally, liquid is rapidly replaced at the transfer area due to the flow profiles redistributing the liquid throughout the tank.
Multiphase mixing (G – L – S)
Three phase systems consist of a solid, liquid and gas phase. Mixers can also be applied in these three phase systems. The mechanism and purpose of mixing remain the same as for two phase system. However, it adds another design element for mixers, as one must optimize for multiple phases. A typical application of a three-phase system is a slurry hydrogenation reactor in the Fischer Tropsch process. Gaseous hydrogen is bubbled through the liquid hydrocarbon phase. The hydrocarbons and hydrogen react together on the surface of a solid catalyst to higher hydrocarbons.


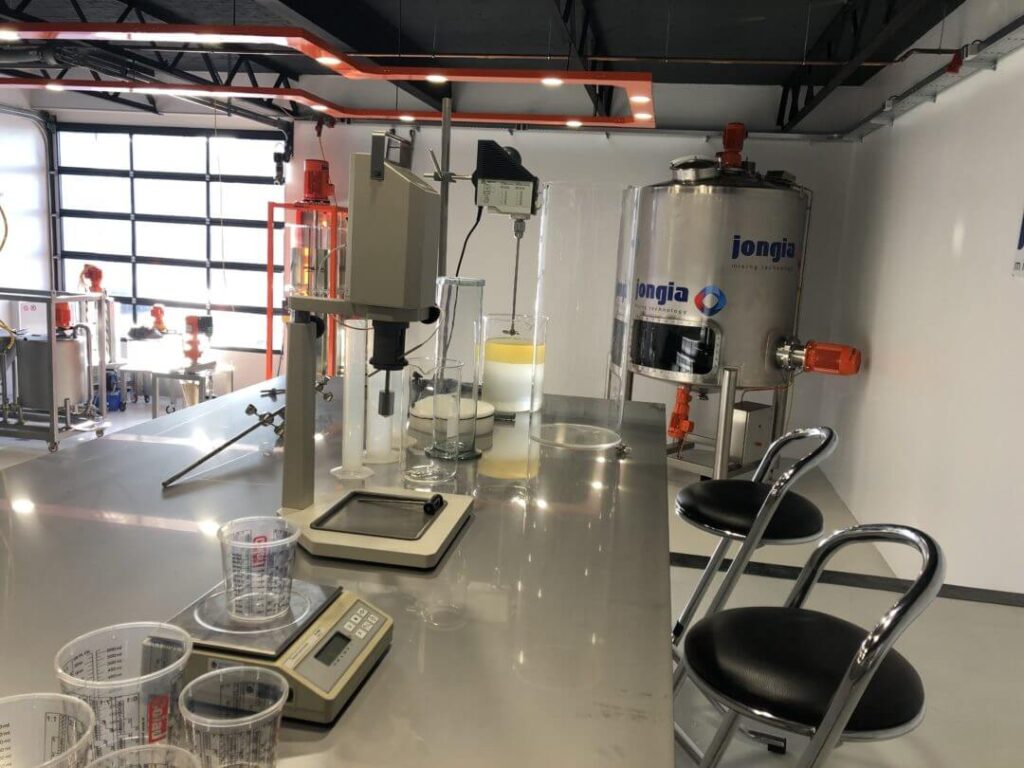
Test Center
Jongia’s (scale) testing facilities enable us to finetune our customer’s process to guarantee the best possible results. In close collaboration with our R&D team, customers have been able to achieve considerable process improvements.

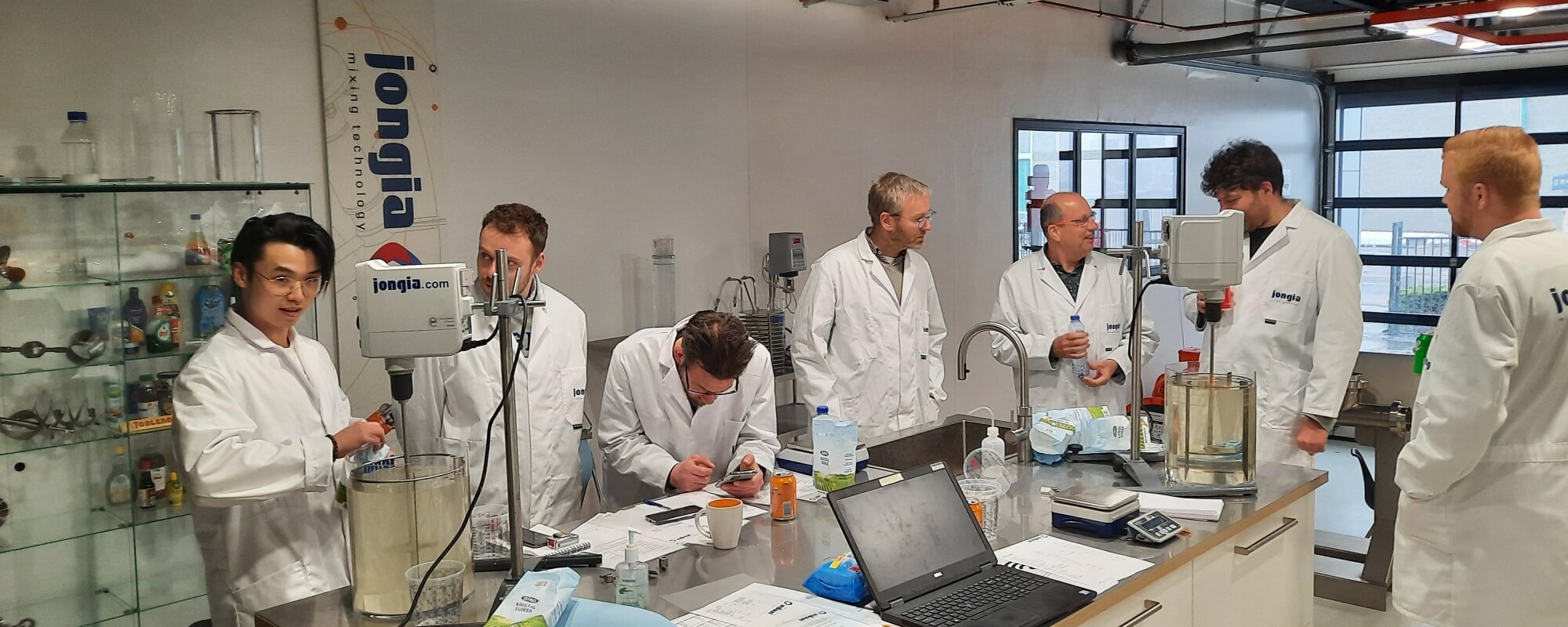
Training
Qualified staff are key to accomplish increased productivity which essentially leads to maximizing your profitability. Jongia can get your staff qualified by providing Agitator technology, Operation and Maintenance training.
Process Optimisation
Think along with you about your process, define each others issues and optimize the process from there out. In this way the process will be better, more smart and efficient, resulting in a much higher and more consistent quality.
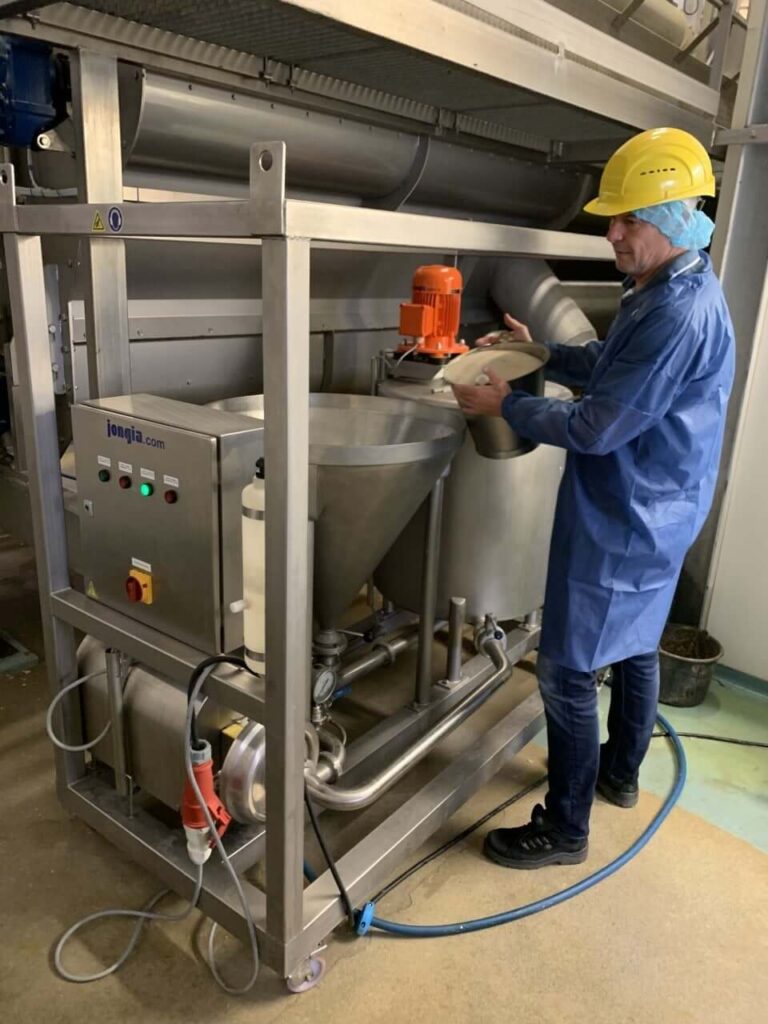
Jongia test units
Rent the Jongia test units to test, optimize and produce the best results!
Measuring is knowing, that’s a well-known fact. It is not always easy to measure process results before an installation is put into use. Jongia’s test units offer the solution. These units are used in particular for the testing of new, innovative processes, for example to develop an entirely new concept. However, it is also common for existing production processes to be simulated on a small scale. The test units make it possible to adjust the process again and again, until it is fully clear which process solution is best. An optimized production process is the result. The use of test units is a very effective approach, which has already led to new production processes, insights and process improvements in many of our relationships.
The test units
Jongia has developed several test units with a capacity of up to 250 litres, in which the most diverse mixing processes are tested. From food to waste water and from chemical cleaners to biogas, the test units are used in many areas. Our process technologists are happy to take up the challenge with you. Together we achieve the best process result. Once that has been achieved, there is much more grip on the process and the ideal situation is then applied industrial scale.
In the Technology Test Center or on location
The test units are for rent and offer you a lot of flexibility. You decide the rental period and the extent to which you require support from our process technologists. In addition, you can choose whether to use the test units on site, or whether you allow the testing process to take place at the Technology Test Center of Jongia.
For more information about the test units, please contact Bart Brouwer or Kevin van Geffen of the Jongia Sales team.

Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the Jongia Technology Center?
The Jongia Technology Center collaborates closely with clients to optimize their processes. By addressing specific issues together, we enhance efficiency and quality, resulting in improved production outcomes and consistent results for various processes.
How does Jongia guarantee the best results for customers?
Jongia fine-tunes customer processes through in-house testing facilities and collaboration with their R&D team. This partnership yields considerable process improvements, ensuring customers achieve optimal results tailored to their specific needs.
What types of mixing processes are tested at Jongia?
Jongia tests several mixing processes, including single-phase blending, emulsification, gas dispersion, and solvation of solids. Our test units can handle diverse materials, enabling the creation of tailored solutions across various industries.
Can customers rent Jongia's test units?
Yes, customers can rent Jongia’s test units, which provide flexibility in testing processes. The duration of the rental can be selected and whether tests are conducted on-site or at Jongia’s Technology Test Center.
What training does Jongia offer for staff?
Jongia offers training in agitator technology, operation, and maintenance. This training ensures that staff are qualified to enhance productivity, which ultimately contributes to maximizing profitability for the organization.
Contact our specialized team for all your questions

Tom Pruymboom
Sales Director
Area Worldwide

Bart Brouwer
Area Sales Manager
Area Worldwide

Masterclass on Mixing & Stirring at Jongia Mixing Technology
At Jongia Mixing Technology, our Masterclass is a training session in our technology center that combines learning with practical experience
Popular Articles

Do I need a Bottom Bearing for my agitator?
Do I need a Bottom Bearing? The installation of a bottom bearing is not mandatory. While it offers certain advantages, there are also drawbacks to consider. It is important to note that the bottom bearing functions more as a displacement

Fermentation & Bioreactor Mixing Process
Bioreactors and Fermenters are culture systems to produce cells or organisms. They are used in various applications, including basic research and development, and the manufacturing of biopharmaceuticals, food and food additives, chemicals, and other products. A broad range of cell types and organisms can be cultivated in bioreactors and Fermenters, including cells (like mammalian cell lines, insect cells, and stem cells), microorganisms (like bacteria, yeasts, and fungi), as well as plant cells and algae. The words “Bioreactor” and “Fermenter” are basically the same thing.

Biodiesel blending with zero leakage!
Fuel blending is a critical component of biodiesel production. A properly blended fuel can increase energy efficiency, reduce emissions and improve performance. However, it can be difficult to achieve consistent fuel quality during blending due to differences in storage tanks,







