Axial Flow Turbine Mixing Element
In order to provide a visual explanation of the operation of the Axial Flow Turbine, we have included a video tutorial. Check it out below!
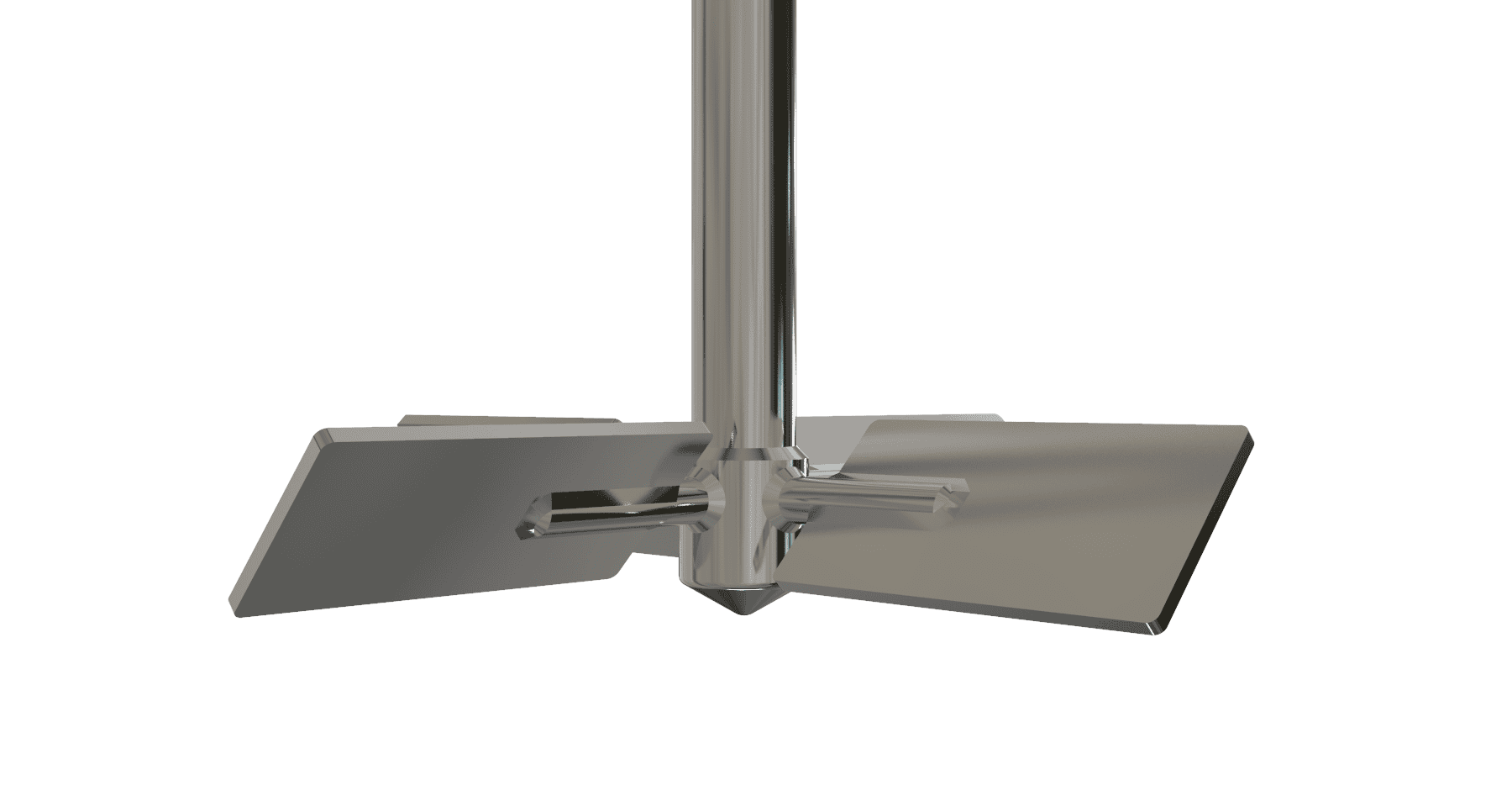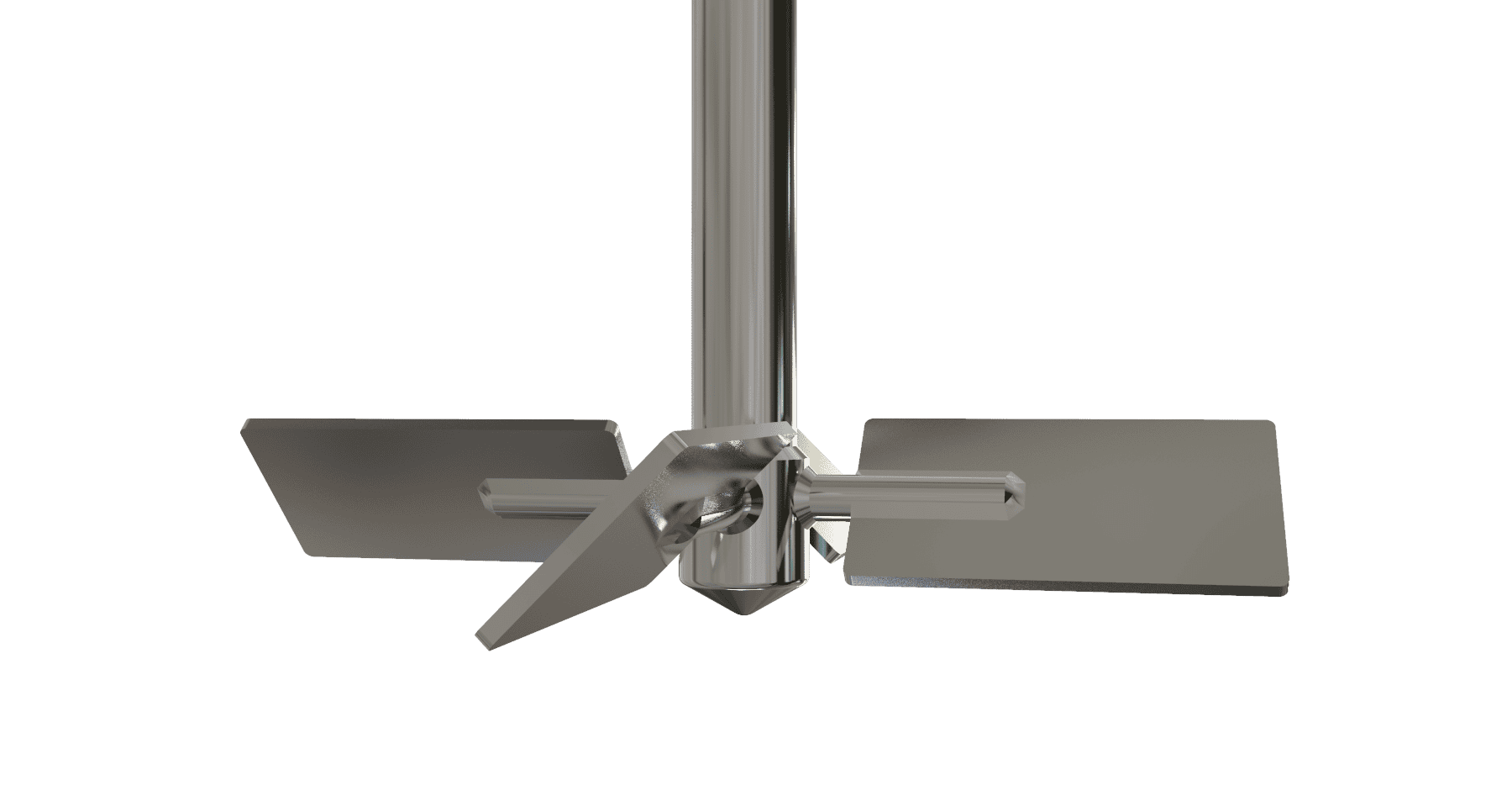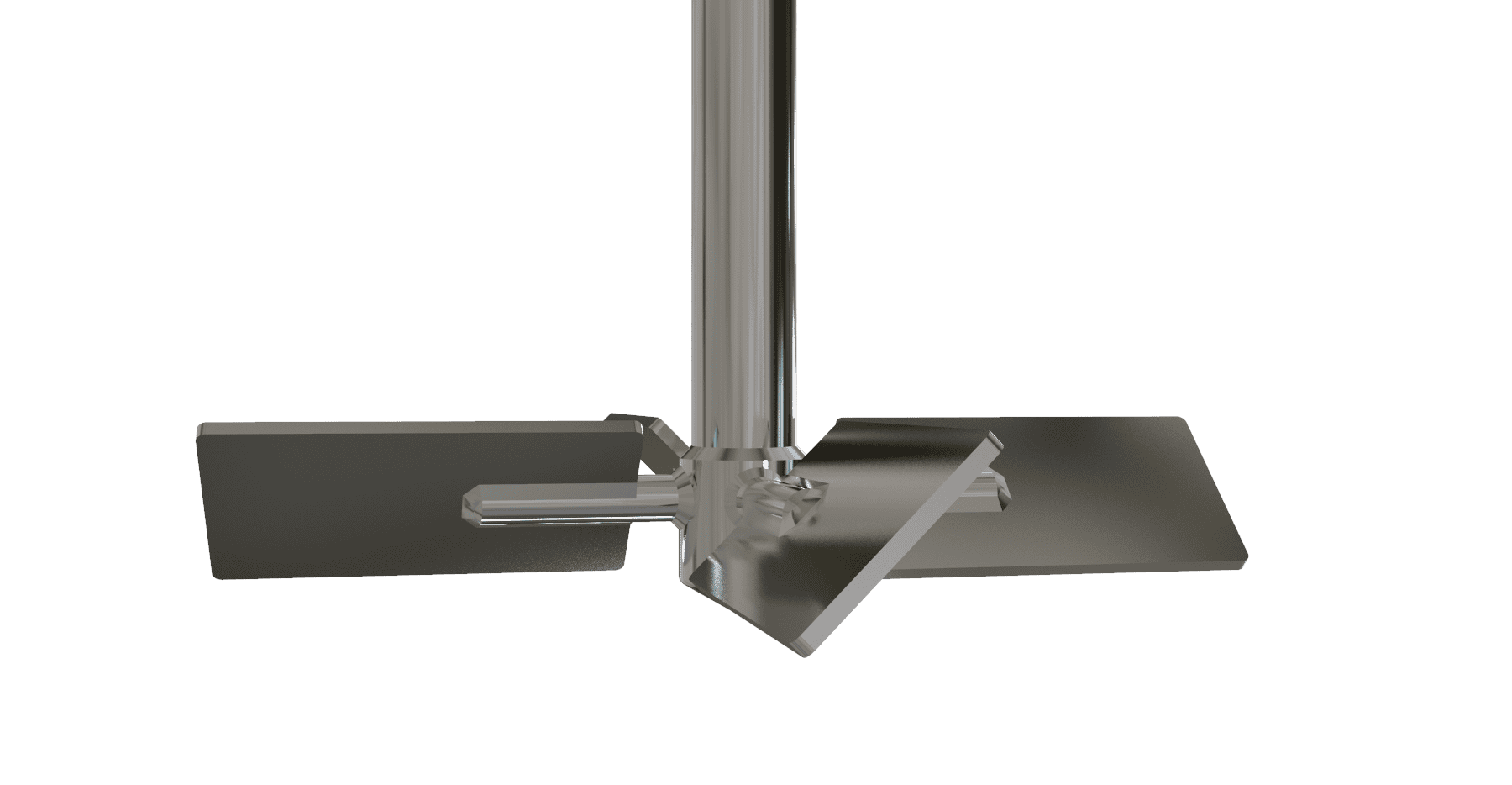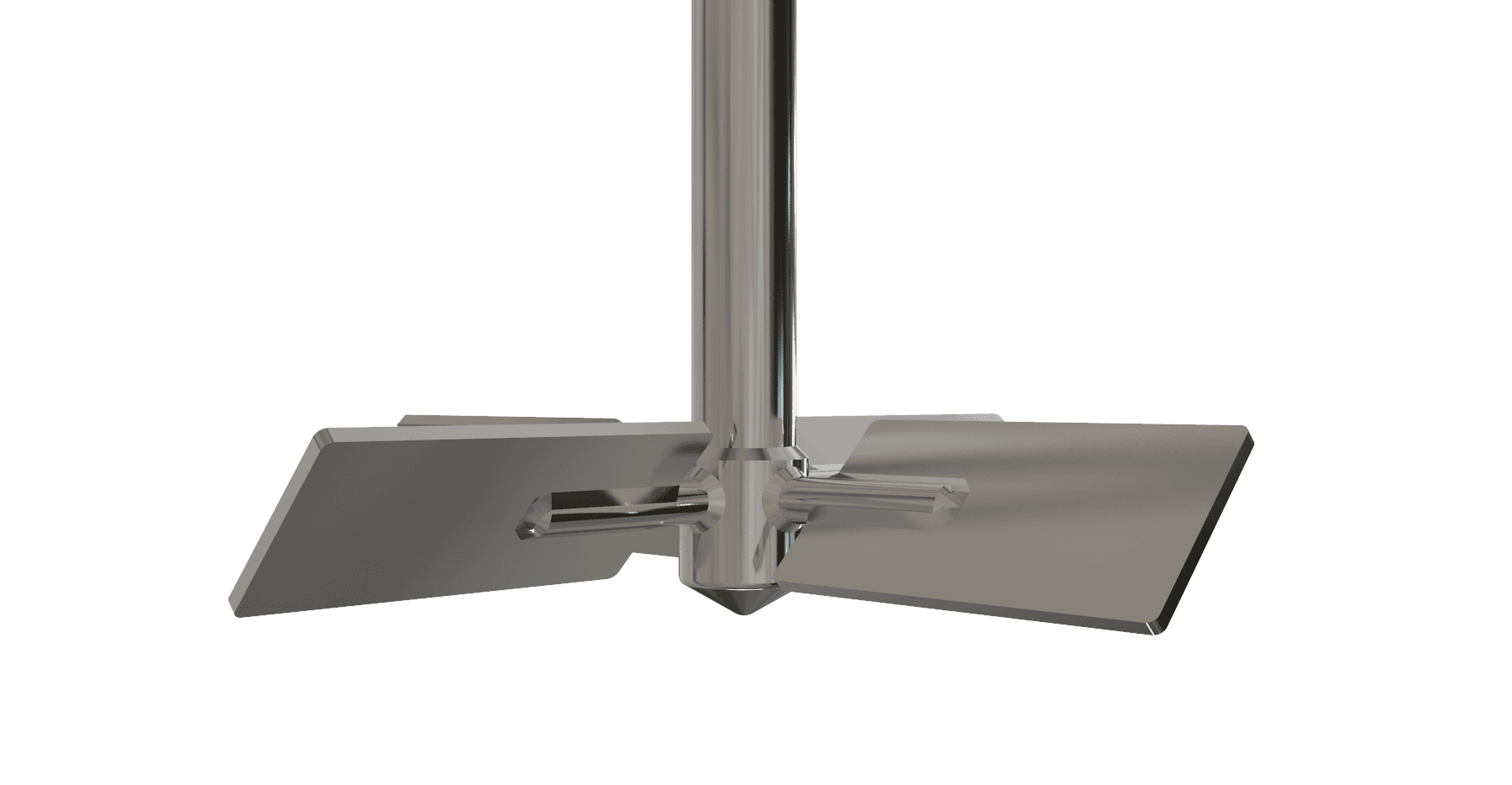
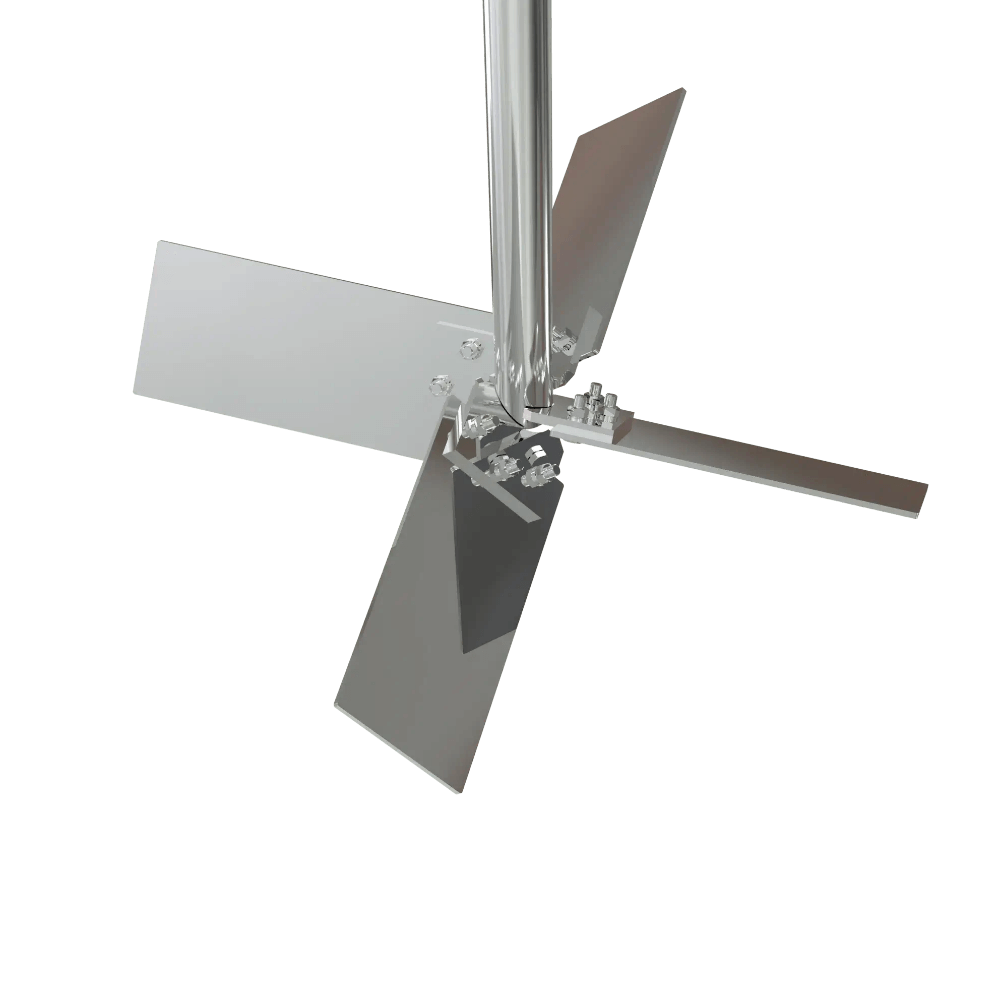
Axial Flow Turbine Bolted
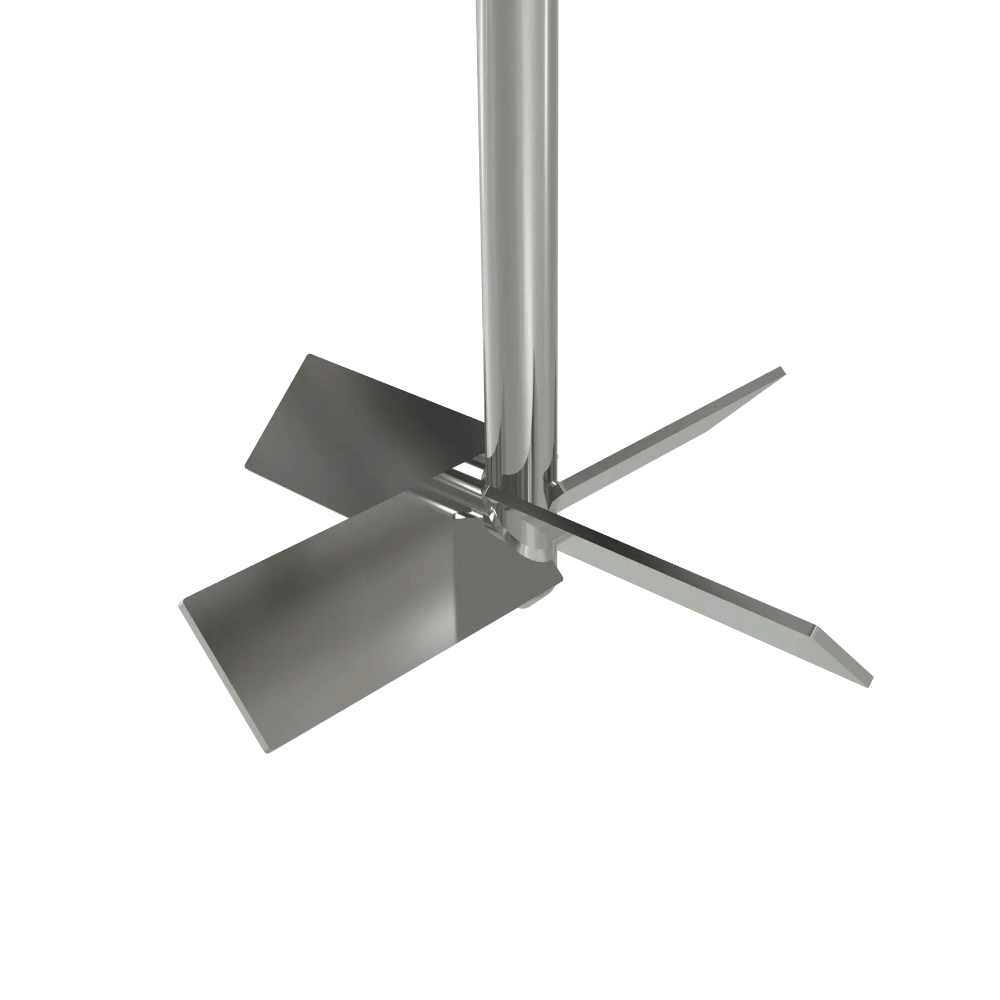

Axial Flow Turbine Welded
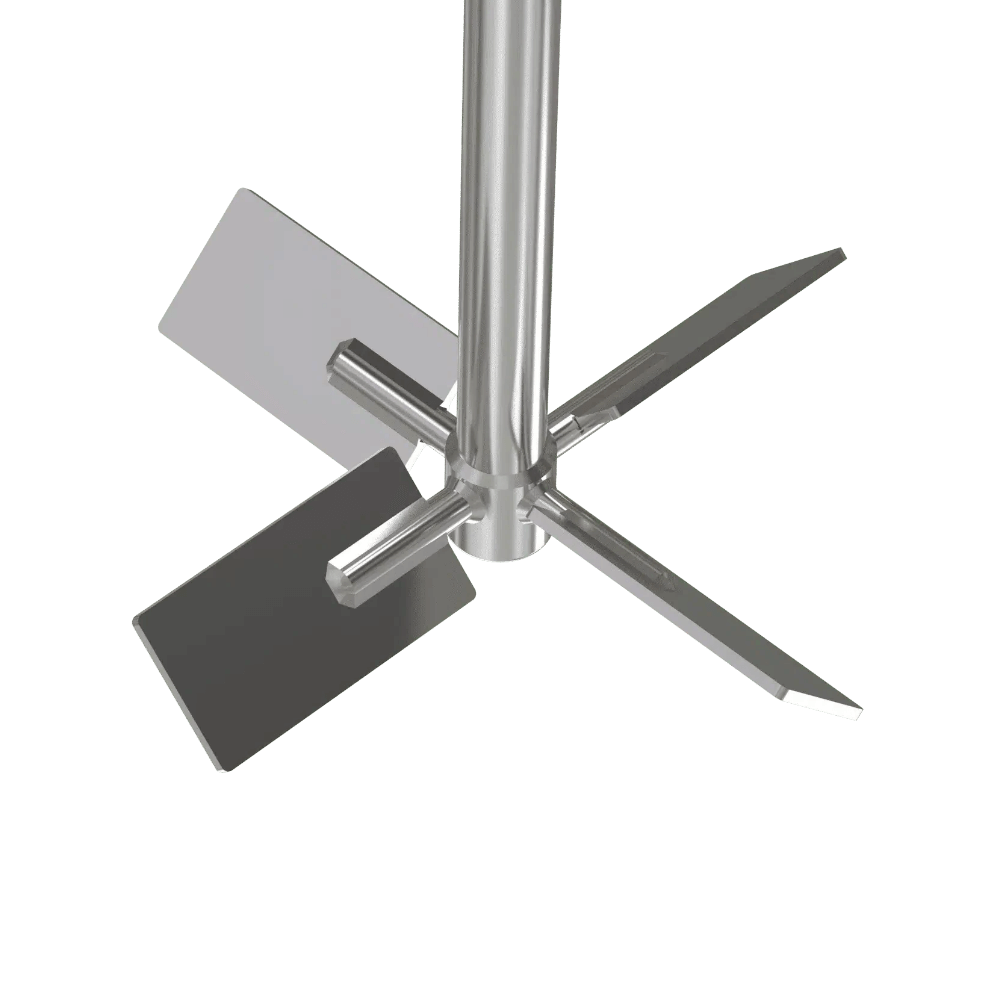
Axial Flow Turbine Pin
Tutorial Axial Flow Turbine
In this tutorial, Commercial Director Tom Pruymboom shows you the process of starch gelatinization using a labscale test unit. In it, raw starch is dissolved in 10 liters of water and the mixture is then heated using a heating coil. When it has become a gel, enzymes are added to convert the mixture to glucose. The mixing is done by a mixer shaft equipped with a 2-blade residual stirrer, a 4-blade Axial Flow turbine and a Hydroprop mixing element for a top-over-bottom stirring process with axial flow.
Related Articles

VVTI Biogas Tilburg
VTTI Biogas Tilburg is developing a new bio-energy facility, focusing on processing organic waste. The plant is expected to produce approximately 23 million cubic metres of biogas annually. A portion of this will be converted into green gas for the

Homogenization and Cooling in Diary Cream Production
Utilizing Jongia’s Cup Mixer Homogenization is a standard procedure employed in dairy cream production to ensure the consistent distribution of fat globules in both milk and cream. This process, achieved through a high-pressure homogenization apparatus, breaks down and disperses fat

Tutorial: Rushton Turbine vs Concave Turbine
We are happy to announce on behalf of Jongia Mixing Technology that we have just launched a new tutorial on our website! This time, we take you into the world of mixing technology with an in-depth comparison between the “Rusthon


