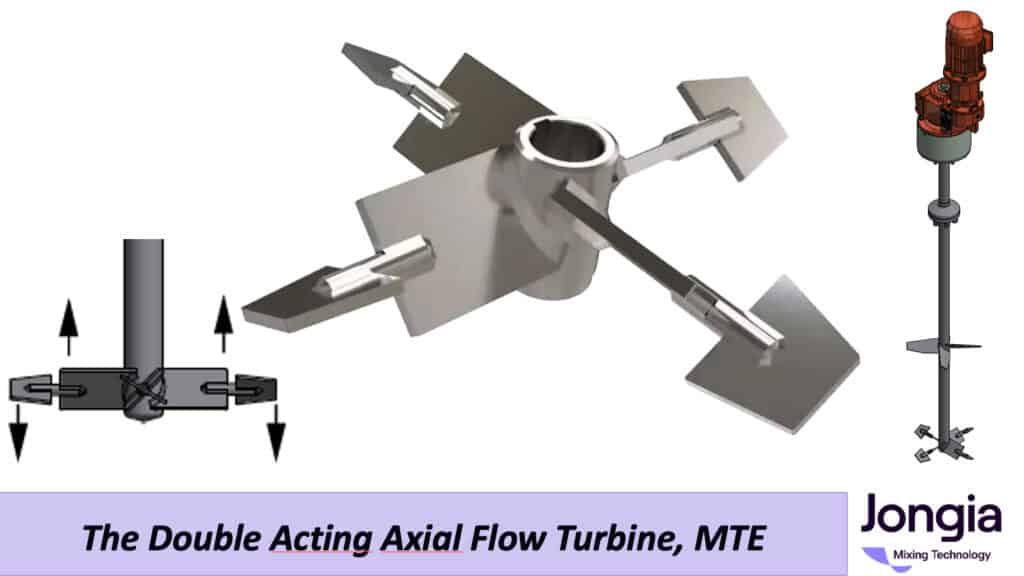
Operation of an AST-MTE Element
Operation of an AST-MTE Element
This element can be used in both CW (clockwise) and CCW (counterclockwise) directions. In one case, the inner AST element is downward-pumping with the outer tips pumping upward, and in the other case, it’s the opposite.
This element is highly effective when dealing with a viscous fluid (often with higher density) into which a thin fluid with lower density needs to be mixed.
Examples
- Dye/water in wall paint (latex) to bring product to specification
- Small amount of water in cold fruit (orange) concentrate to achieve the correct Brix number for customer delivery
- Solvent in primer paint to achieve the correct dry solids content
In summary: thin, light fluid into thick, heavy fluid.
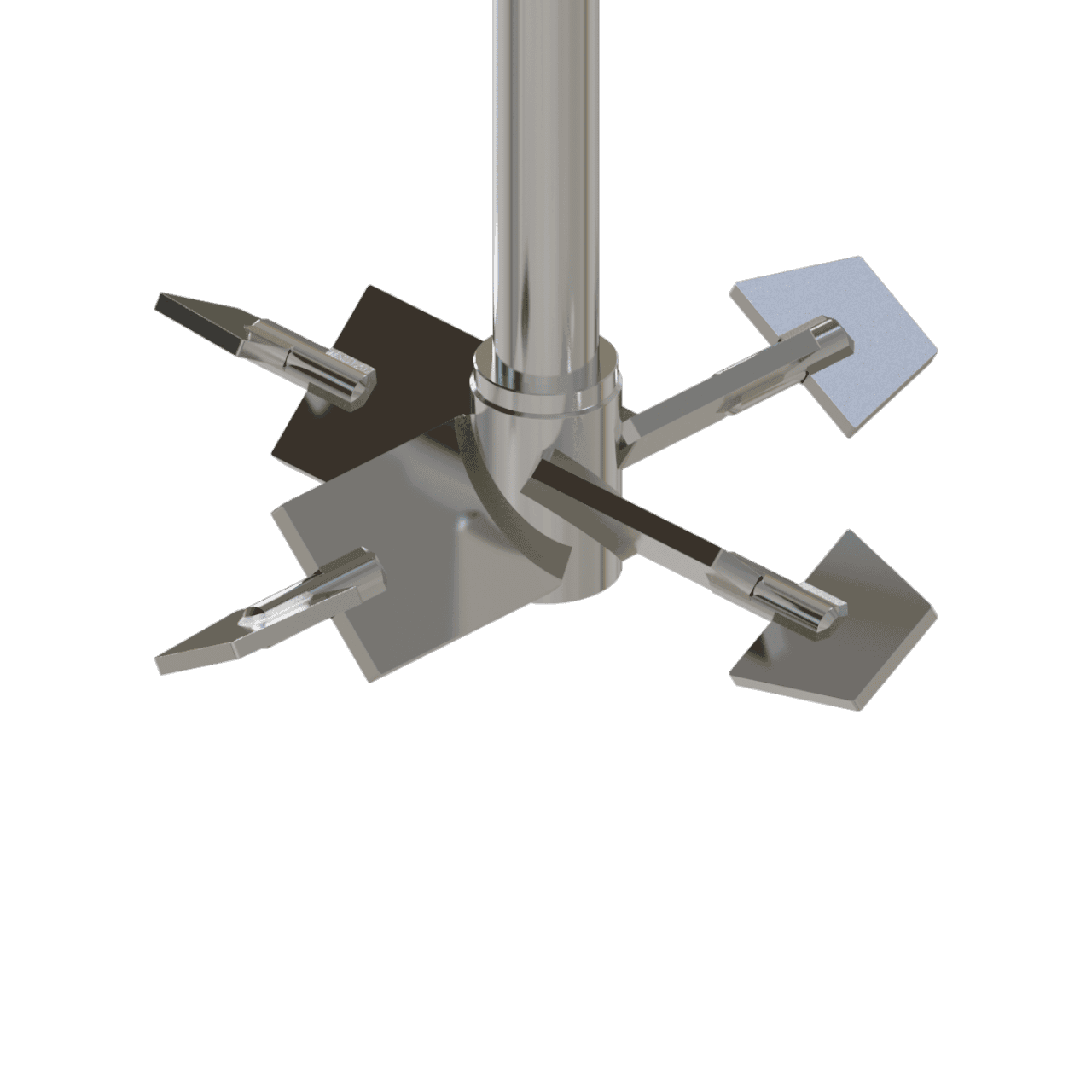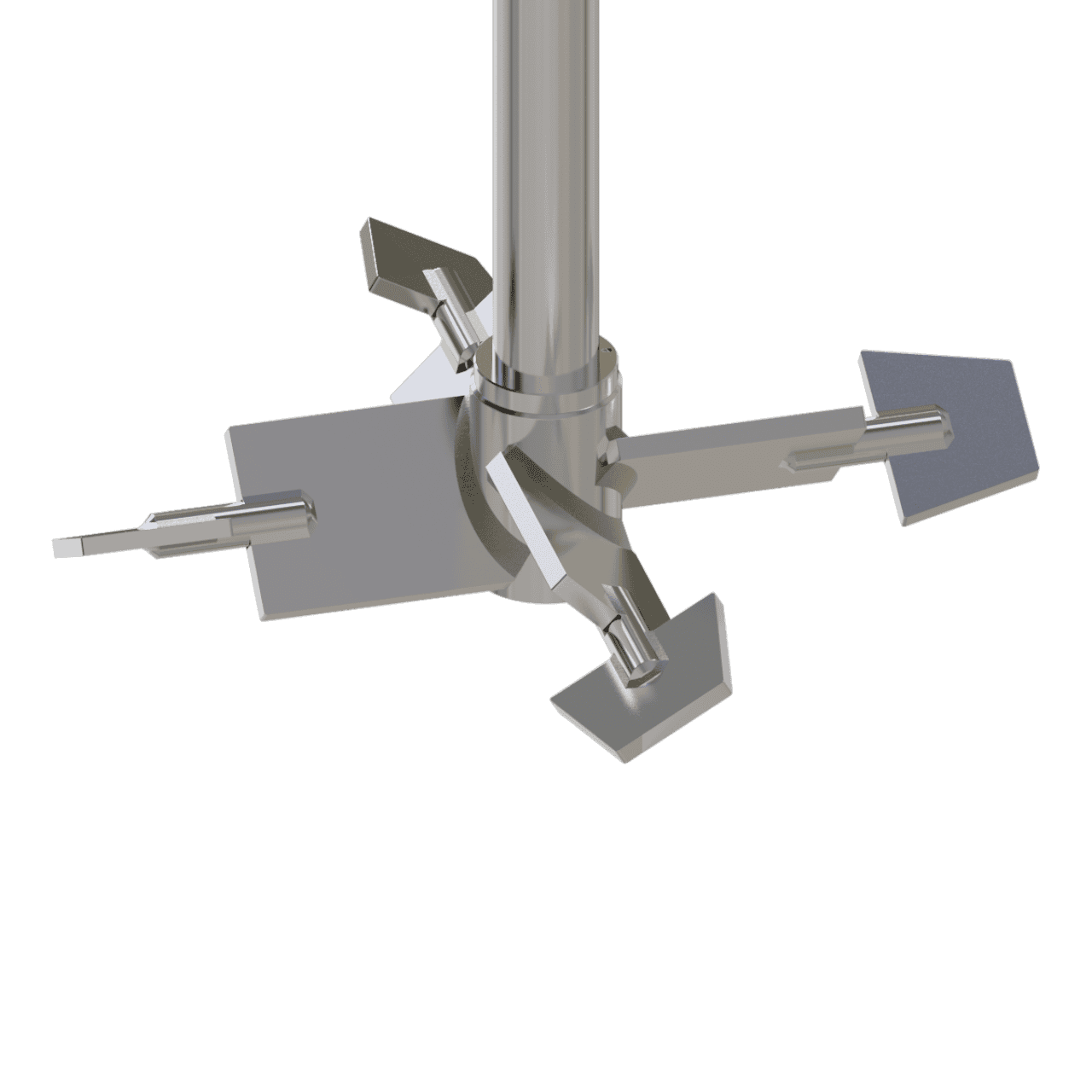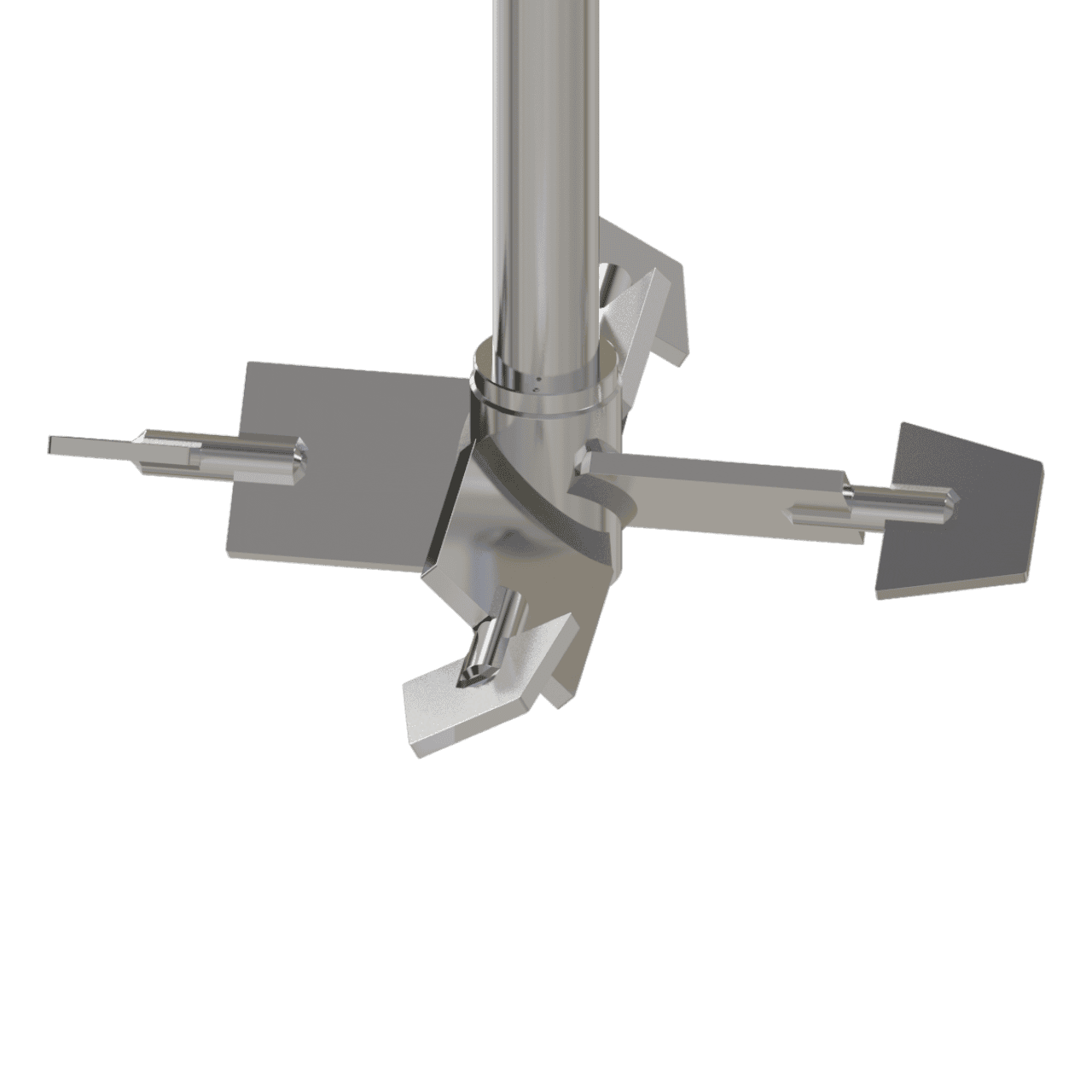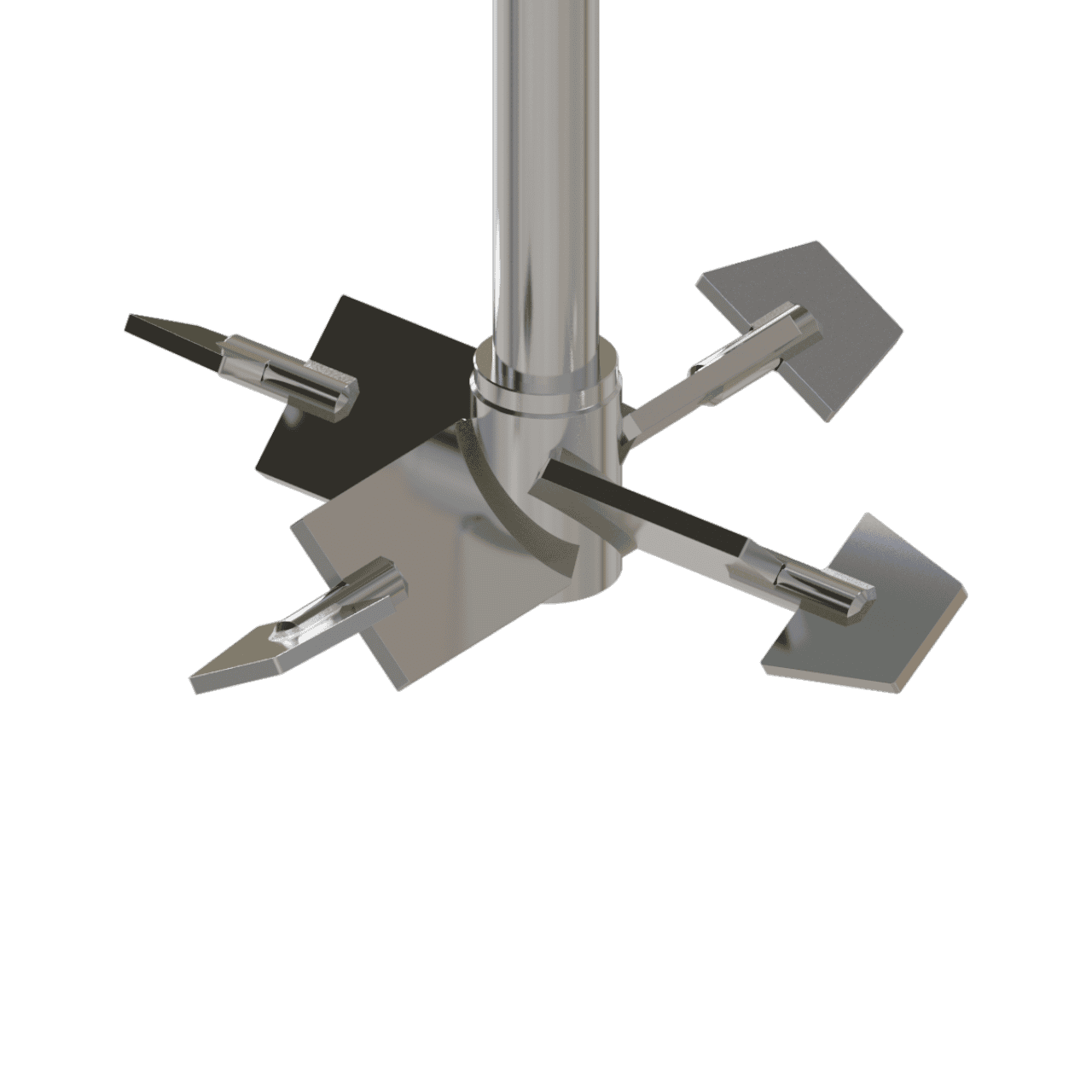
Technical Operation
It all starts with a pitched blade mixing turbine as often used in mixing and blending processes. However, in some cases a pitched turbine alone is not always capable of mixing the thin fluid with the thick fluid, therefor sometimes ending us with the thin fluid remaining as a pocket around the turbine mixing element.
Thus, by adding inversely pumping tips on each of the pitched turbine blades, good interaction is achieved between the thin fluid and the bulk fluid at the blade tips, enabling transport of the thin fluid inwards towards the thick fluid. In this configuration, the inner mixing blade is pumping downward and the outer mixing blade is pumping upward.
In more heavily cases where more flow across the bottom of the tankvessel is required (for example, with solids or stagnant zones in the extreme corner), the pumping direction (or configuration or rotation direction) can be reversed to achieve an even better result.
It’s conceivable that some processes require both directions, which can be easily achieved by reversing the direction of rotation.

Key Advantages
- Fast mixing
- Moves smoothly through the fluid surface
- Operates stably
- Simple construction
Benefit
This turbine requires hardly any more power intake if compared to the genuine axial flow turbine Mixing Element.
Is this worthwhile for you process optimization? Give it a try!
Let Jongia help you and contact: sales@jongia.com
Contact our specialized team for all your questions

Tom Pruymboom
Sales Director

Teun van der Spek
Area Sales Manager

Our History
From the moment Jongia was founded in 1937 we have been evolving structurally over the years. Learn more about our company’s history with the summary of most important moments highlighted in a timeline.
Related News

High-Speed Disperser Technology: The Engineering Behind Effective Mixing
A Technical Guide by Jongia Mixing Technology Core Function High-speed dispersers excel at three critical tasks: Fracturing powder agglomerates into fine particles Creating uniform powder distribution throughout liquid mediums Facilitating complete dissolution of soluble materials Operating Principles High-speed dispersers transform

VVTI Biogas Tilburg
VTTI Biogas Tilburg is developing a new bio-energy facility, focusing on processing organic waste. The plant is expected to produce approximately 23 million cubic metres of biogas annually. A portion of this will be converted into green gas for the

Homogenization and Cooling in Diary Cream Production
Utilizing Jongia’s Cup Mixer Homogenization is a standard procedure employed in dairy cream production to ensure the consistent distribution of fat globules in both milk and cream. This process, achieved through a high-pressure homogenization apparatus, breaks down and disperses fat




